What are Normal PSA Levels by Age?
Author: Brian Hildebrandt
The normal range of PSA levels tends to increase as a man ages, with some minor variation between races.
High PSA test results will generally give your first indication of prostate cancer, alongside a positive Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) – another prostate cancer test.
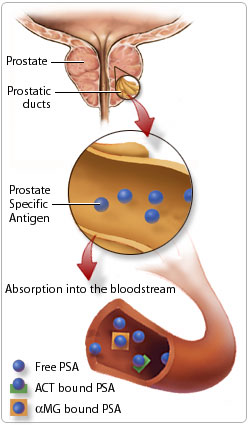
PSA aka Prostate Specific Antigen is a protein enzyme produced in the prostate gland and released in to the blood stream.
After blood work analysis, the resulting PSA score shows how much of the enzyme you’re producing, and your probability of being diagnosed with prostate cancer.
Normal PSA Ranges by Age
| Age (Years) | Asian (ng/mL) | African (ng/mL) | Caucasian (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 – 49 | 0 – 2.0 | 0 – 2.0 | 0 – 2.5 |
| 50 – 59 | 0 – 3.0 | 0 – 4.0 | 0 – 3.5 |
| 60 – 69 | 0 – 4.0 | 0 – 4.5 | 0 – 4.5 |
| 70 – 79 | 0 – 5.0 | 0 – 5.5 | 0 – 6.5 |
Unit Conversion Calculator
PSA Level Risk Analysis
- 15% of men with a PSA level less than 4 ng/ml go on to develop prostate cancer.
- 31% of men with PSA levels between 4 – 10 ng/ml have shown to develop prostate cancer.
- 50% – 65% of men with psa scores over 10 ng/ml develop prostate cancer.
An important part of the your results is finding both the;
1. Total amount of PSA in your blood.
2. Ratio of free vs bound PSA.
Positive PSA Score Association with Other Conditions
The amount of PSA in your blood test may increase with other prostate conditions such prostatitis, enlarged prostate (BPH), or within two days after ejaculation.
Rest assured, even though your results may be high, it doesn’t necessarily mean you have prostate cancer. Just a greater risk of developing it.
Elevated PSA Range - Prostate Cancer Test
- Normal PSA Levels: 0 - 4 ng/mL
- Slightly Elevated PSA: 4 - 10 ng/mL
- Moderately Elevated PSA: 10 - 20 ng/mL
- Highly Elevated PSA: 20+ ng/mL
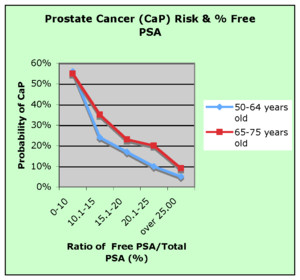
PSA Levels by Age Chart (Free to Total Ratio)
The main difference between the PSA scores of prostatitis and an enlarged prostate, compared to prostate cancer, is the ratio of free vs bound PSA within your test sample.
- Prostate Cancer will have a higher bound PSA ratio.
- An enlarged prostate and prostatitis will have a higher free PSA ratio.
- If your free PSA results are less than 25%, your risk for developing prostate cancer is between 10% to 20%.
- If your free PSA results are less than 10%, your risk for developing prostate cancer jumps to around 50%.
PSA Test Velocity (PSA-V)
The faster your PSA score increases over time, the greater your chances of developing prostate cancer. It may be a good idea to track your PSA over time, to determine your risk.
Average PSA Test Doubling Time (PSA-DT)
Another red flag. This calculation denotes the time it takes your PSA values to double.
Therefore it may signify the aggressiveness of any prostate abnormalities, whether it's an enlarged prostate, prostatitis, or prostate cancer.
If your average PSA readings double in less than three years your doctor will most likely order a biopsy, to look in to the problem further and discuss possible prostate cancer treatment options.